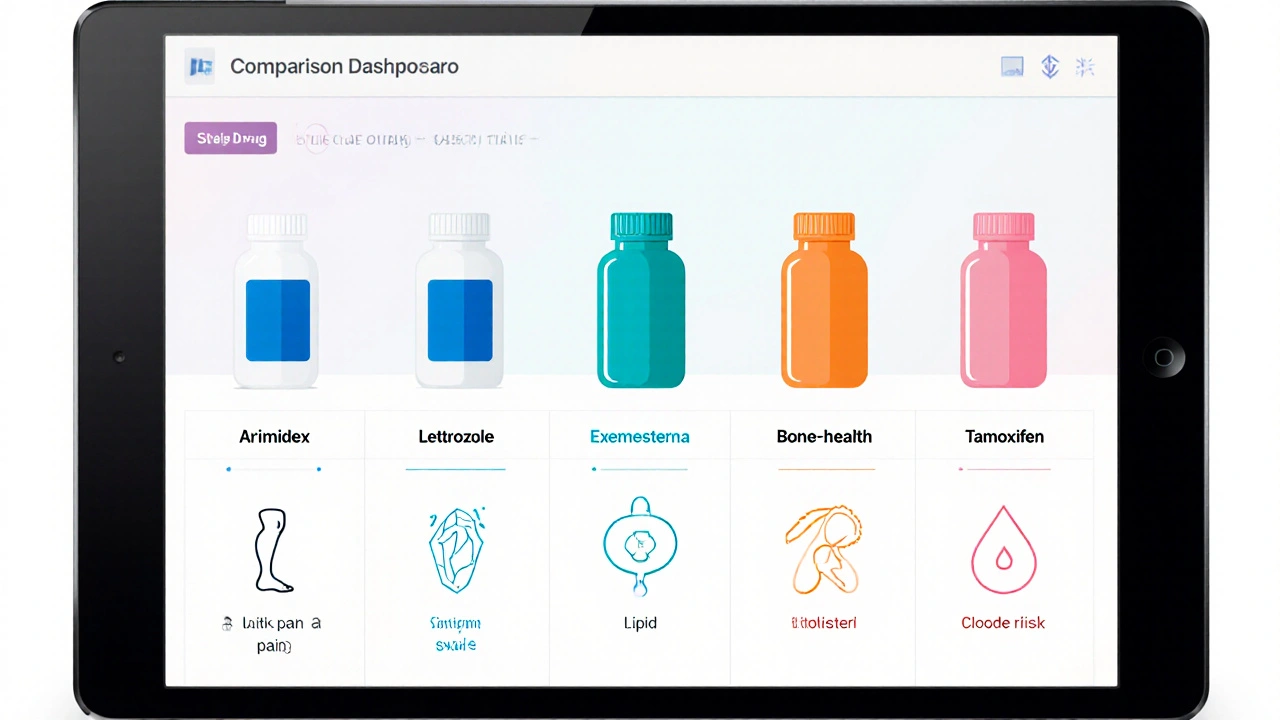
Aromatase Inhibitor Comparison Tool
Select a medication to compare its key characteristics:
Arimidex (Anastrozole)
Third-generation non-steroidal AI
Letrozole
Third-generation non-steroidal AI
Exemestane
Steroidal AI
Tamoxifen
Selective estrogen receptor modulator
Common Side Effects
Key Differences
TL;DR
- Arimidex (anastrozole) is a third‑generation aromatase inhibitor (AI) taken daily to lower estrogen in post‑menopausal breast cancer patients.
- Letrozole is slightly more potent but requires a 2.5mg weekly pulse for some regimens; side‑effects overlap heavily.
- Exemestane is a steroidal AI with a once‑daily dose, often chosen after resistance to non‑steroidal AIs.
- Tamoxifen works by blocking estrogen receptors rather than lowering estrogen; useful in pre‑menopausal patients or as a sequential therapy.
- Choosing the right AI depends on disease stage, prior AI exposure, bone health, and cost considerations.
When it comes to hormone‑responsive breast cancer, Arimidex is a selective aromatase inhibitor that blocks the enzyme aromatase, reducing estrogen production in post‑menopausal women. Approved by the FDA in 1995, it has become a cornerstone of adjuvant therapy for estrogen‑receptor‑positive (ER+) tumors. But the market also offers letrozole, exemestane, and older agents like tamoxifen. This article walks through how each option works, where they shine, and what side‑effects you might expect, so you can decide which drug matches your health profile and lifestyle.
How Aromatase Inhibitors Work
Aromatase inhibitors (AIs) target the enzyme aromatase, which converts adrenal‑derived androgens into estrogen. In post‑menopausal women, most estrogen comes from this peripheral conversion, so shutting down aromatase dramatically cuts circulating estrogen levels. Lower estrogen deprives ER+ cancer cells of their growth signal, slowing or stopping tumor progression.
The AI class splits into two chemical families:
- Non‑steroidal AIs - include anastrozole and letrozole; they bind reversibly to the aromatase active site.
- Steroidal AI - exemestane mimics the natural substrate and inactivates the enzyme permanently (irreversible binding).
Understanding the distinction helps explain why some patients switch from a non‑steroidal AI to exemestane after disease progression - the different binding mode can overcome resistance.
Arimidex (Anastrozole) - Core Facts
Anastrozole is marketed under the brand name Arimidex. Its key attributes are:
- Dosage: 1mg orally once daily.
- Half‑life: Approximately 50hours, allowing steady plasma levels.
- Efficacy: In the ATAC trial, anastrozole reduced recurrence by ~30% compared with tamoxifen.
- Common side‑effects: Joint pain, hot flashes, mild bone density loss.
- Cost (2025, US): $150‑$200 per month for the generic version.
Because it’s taken daily, adherence is generally good, but patients report occasional insomnia due to night‑time sweating. Routine bone‑density monitoring is advised, especially for women with pre‑existing osteoporosis.
Letrozole - The More Potent Peer
Letrozole is another third‑generation non‑steroidal AI, often dubbed the “stronger” cousin of anastrozole. Its profile includes:
- Dosage: 2.5mg orally once daily (or 10mg weekly in some extended‑dose protocols).
- Half‑life: Around 2days, slightly longer than anastrozole.
- Efficacy: In the BIG 1‑98 trial, letrozole showed a modest 4‑5% absolute improvement in disease‑free survival over anastrozole.
- Side‑effects: Similar to anastrozole but with a higher incidence of severe joint stiffness and cholesterol elevation.
- Cost (2025, US): $180‑$230 per month for the generic.
Both drugs suppress estrogen to <10pg/mL on average, but letrozole may achieve slightly lower levels, which can be beneficial in high‑risk patients. The trade‑off is a marginally higher risk of cardiovascular changes.
Exemestane - The Steroidal Option
Exemestane is a steroidal AI that binds irreversibly to aromatase. Its distinguishing points are:
- Dosage: 25mg orally once daily.
- Half‑life: About 24hours, but the enzyme remains inactivated for days.
- Efficacy: The INTERGROUP S-III trial showed exemestane lowered recurrence after five years of tamoxifen by roughly 10%.
- Side‑effects: Joint pain comparable to other AIs, but a slightly lower impact on bone turnover - some studies report modest bone‑density preservation.
- Cost (2025, US): $140‑$190 per month for generic.
Because of its steroidal nature, exemestane is often reserved for patients who have progressed on non‑steroidal AIs, offering a “different mechanism” to bypass resistance.
Tamoxifen - The Classic Antagonist
Tamoxifen isn’t an AI; it’s a selective estrogen‑receptor modulator (SERM). It blocks estrogen receptors in breast tissue while acting as an estrogen agonist in bone and the uterus. Key facts:
- Dosage: 20mg orally once daily for five years (standard adjuvant course).
- Efficacy: Pioneering trials in the 1970s demonstrated a 40‑50% reduction in recurrence compared with placebo.
- Side‑effects: Hot flashes, increased risk of venous thromboembolism, and a small rise in endometrial cancer incidence.
- Cost (2025, US): $30‑$50 per month for generic.
Tamoxifen remains a go‑to for pre‑menopausal women and for those who cannot tolerate AI‑related bone loss. Some clinicians use sequential therapy - five years of tamoxifen followed by an AI - to balance benefits.
Comparison Table
| Drug | Class | Typical Dose | Estrogen Suppression (% of baseline) | Primary Side‑effects | Cost (US, 2025) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Arimidex (Anastrozole) | Non‑steroidal AI | 1mg daily | ≈95% | Joint pain, hot flashes, mild bone loss | $150‑$200/mo |
| Letrozole | Non‑steroidal AI | 2.5mg daily | ≈97% | Joint stiffness, cholesterol rise | $180‑$230/mo |
| Exemestane | Steroidal AI | 25mg daily | ≈93% | Joint pain, slightly lower bone impact | $140‑$190/mo |
| Tamoxifen | SERM | 20mg daily | ~70% (receptor blockade) | Hot flashes, clot risk, uterine issues | $30‑$50/mo |
Choosing the Right Agent for You
Decision‑making isn’t just about numbers; it’s about your overall health picture.
- Bone health - If you have osteoporosis, letrozole’s higher bone‑loss risk might steer you toward exemestane or add a bisphosphonate.
- Cardiovascular profile - Patients with high cholesterol may prefer anastrozole over letrozole.
- Prior AI exposure - After progression on a non‑steroidal AI, switching to exemestane often restores response.
- Cost & insurance coverage - Generic anastrozole and tamoxifen are usually the cheapest; letrozole can be pricier unless covered.
- Menopausal status - Pre‑menopausal women need tamoxifen or ovarian suppression before an AI can work.
Talk with your oncologist about baseline DEXA scans, lipid panels, and personal preferences. Shared decision‑making improves adherence and outcomes.
Potential Pitfalls and How to Avoid Them
- Skipping bone‑density checks: Even mild estrogen suppression can accelerate bone loss. Schedule a DEXA scan at baseline and then every 1‑2years.
- Ignoring drug interactions: Antacids containing aluminum or calcium can lower AI absorption - take the pill on an empty stomach.
- Not reporting joint pain early: Physical therapy, NSAIDs, or switching to a different AI can help.
- Assuming all AIs are interchangeable: Resistance mechanisms differ; a switch is not always a simple swap.
Frequently Asked Questions
Can I take Arimidex and letrozole together?
No. Both drugs suppress the same enzyme, so combining them offers no extra benefit and raises the risk of side‑effects. Your doctor will pick the one that best fits your health profile.
How long should I stay on an AI after surgery?
Standard guidelines recommend five years of AI therapy for most post‑menopausal patients. Some high‑risk cases extend to ten years, but that decision depends on tumor grade and genetic factors.
Is exemestane safe for women with a history of heart disease?
Exemestane has a slightly lower impact on cholesterol than letrozole, making it a reasonable option for patients with controlled cardiovascular disease. Still, regular lipid monitoring is advised.
Do I need to stop taking calcium supplements while on an AI?
Don’t stop calcium, but space the timing. Take the AI at least two hours apart from calcium or antacid tablets to ensure proper absorption.
What signs indicate I should switch from anastrozole to exemestane?
If imaging shows disease progression while on anastrozole, especially after 2‑3years, doctors often consider switching to exemestane to target a different mechanism.
In the end, there’s no one‑size‑fits‑all answer. Arimidex offers a convenient, well‑studied option for many post‑menopausal patients, but letrozole, exemestane, and tamoxifen each bring unique strengths. By weighing efficacy, side‑effects, bone health, and cost, you can partner with your care team to pick the therapy that keeps cancer at bay while preserving quality of life.
Wow, a whole interactive tool for comparing aromatase inhibitors – because clearly we all have the free time to click through side‑effect palettes while waiting for chemo.
But hey, kudos for making the data look pretty; the colors really scream “I care about your joint pain”.
Just don’t expect this to replace a good old‑fashioned doctor’s advice, unless you enjoy DIY oncology.
Reading through the tables reminded me of how fragile the balance between efficacy and quality of life really is, and it’s good to see the nuances laid out.
All these pharma giants are just pulling strings, the real cure is hidden in plain sight-don’t trust the mainstream.
The presentation is adequate, yet the terminology could be streamlined; the half‑life figures are precise, but the phrasing "approximately 50 hours" feels verbose when a simple "~2 days" would suffice.
good info but keep it short its a lot to read
Hey folks! 🌟 This tool is awesome!! It gives you the power to compare drugs at a glance!! Remember to check bone density regularly, especially with Arimidex – it’s crucial!! Stay proactive and keep those questions coming!!
Nice job on the layout! 👍👍 The side‑effect icons are super helpful 😁. Just a heads‑up: for patients with pre‑existing osteoporosis, monitoring should be extra rigorous. 📊
From a clinical standpoint, the comparative efficacy data aligns with the ATAC and BIG 1‑98 trial outcomes. The inclusion of cost metrics is also valuable for shared decision‑making, particularly in resource‑limited settings.
Alright, let me break this down for the masses, because apparently a glossy web widget isn’t enough. First, Arimidex is the "easy" choice – one pill a day, half‑life long enough that you can forget you’re even taking it, which is great if you have the memory of a goldfish. Second, let’s talk about Letrozole – it’s marginally more potent, sure, but that translates into a higher chance of severe joint stiffness, something that will make you groan louder than a teenager with a broken Wi‑Fi router. Third, Exemestane, the steroidal newcomer, binds irreversibly – fancy words for “once you’re on it, the enzyme is toast”, and while that sounds cool, it also means you’re paying a premium price without a dramatic boost in survival for most patients.
Now, the cost factor: the numbers don’t lie; Arimidex sits at $150‑$200, Letrozole nudges up to $230, and Exemestane sits comfortably at $250. Yes, you read that right – a $50 bump for a drug that isn’t necessarily better for the average patient. Then there’s Tamoxifen, the old‑timer, cheap as chips at $30‑$50, but it brings its own party tricks: clot risk and endometrial hyperplasia, which are not exactly party favors. Bone health is another nightmare – the mild loss with Arimidex can become a full‑blown osteoporotic dilemma over years; keep that DEXA scan handy.
In short, there is no one‑size‑fits‑all. Your oncologist will weigh disease stage, prior AI exposure, and your personal bone density before tossing a script your way. And if you’re wondering why all these details matter – because the side‑effects are real, they affect adherence, and adherence decides whether the drug actually works. So, choose wisely, get your labs done, and maybe don’t rely solely on a pretty interactive chart to make a life‑changing decision.
Honestly these AI thingz are just a big money grab dont trust the pharma bros.
While the comparison chart does a decent job of listing side‑effects, it utterly fails to capture the emotional toll of chronic joint pain – a reality many patients drown in, day after day, as they grapple with the relentless reminder that their cure is also their curse.
Stick to the plan, monitor bone health, and keep open communication with your care team.
Fantastic effort! The use of vibrant visuals coupled with succinct data points makes the decision‑matrix both accessible and engaging; kudos to the developers for such a polished interface!
Great job on integrating cost analysis; patients often overlook this aspect, yet it can be a decisive factor in therapy adherence, especially in low‑income regions.
The tool leverages a modular UI framework, enabling dynamic data binding; however, the absence of real‑time pharmacogenomic input limits its precision in personalized oncology.
Convenient UI, but it glosses over the complexity of endocrine resistance mechanisms.
Useful summary, thanks.
In the grand tapestry of oncologic therapeutics, one must not merely glance upon superficial metrics, but rather contemplate the philosophical ramifications of hormonal modulation; hence, I posit that this comparative instrument, while aesthetically commendable, demands a deeper epistemological foundation.
While the presentation is polished, several typographical inconsistencies undermine its credibility; for instance, the errant use of "approximately" alongside precise numeric ranges is contradictory.
People should read more and not blindly trust big pharma.